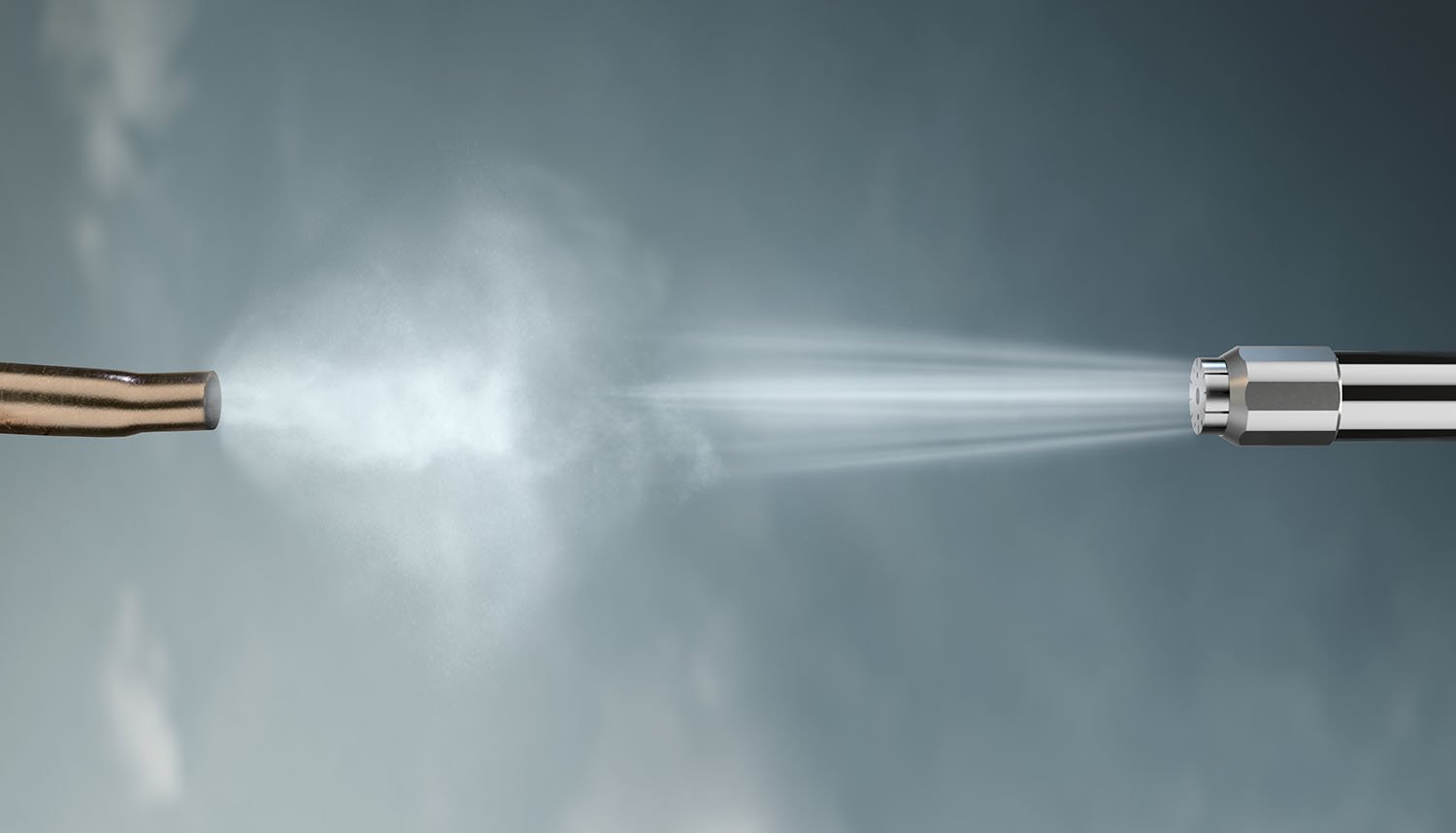
Sound is the result of pressure variations in the air. These pressure variations set the eardrum into motion and produce what we humans perceive as sound. The sound is transmitted from the eardrum through the ossicles to the cochlea where it is converted into electrical signals that continue on to the brain. The human ear can distinguish sound pressure within a very large area. A special measuring scale is used to describe the strength of the sound in the working area of the ear. The result—the sound pressure level—is expressed in decibels (dB).
Sound frequencies
Sound travels at different frequencies (oscillations per second) and the sensitivity of the human ear to them varies. The instrument (sound level meter) used to measure noise is designed to take this into account. The measurement result is filtered and given in an A-weighted level to resemble the sound pressure that the human ear experiences. The resulting sound level is then stated in dB(A). There is also filtering according to a C-weighted level that is used for high-frequency sounds; the result is then stated as dB(C).
In most environments, the sound level varies during the time spent in it, which is taken into account by using a type of average sound level, called the equivalent sound level (Seq), for a period of time, such as an eight-hour workday.
How does several sound sources effect the sound level?
In the logarithmic sound pressure scale, two equally strong sources of sound provide a sound pressure level that is 3 dB higher than just one source. Ten equally strong sources of sound provide a level that is 10 dB higher and one hundred equally loud sources of sound cause a 20 dB higher level. Click here to read our basic information about decibel (dB).

The following formula can be used to calculate the total sound pressure level of several equally strong sources of sound: Lp (total) = Lp + 10*lg(n)
where (n) is the number of equal sources and Lp is the sound pressure level from a source.